Deploying a static website in Azure Static Web Apps
Nowadays JAMStack is trendy because a lot of reasons: performance, security, decoupling, etc.
JAMStack consists of pre-rendering your website or application’s frontend and get the dynamic data from an API.
Your pre-rendered markup can be host in a server, but as it is static, your host only needs to serve static files, just HTML, CSS, and JS. You don’t need to run any code on the server.
There are a lot of different options to deploy a static website, for example:
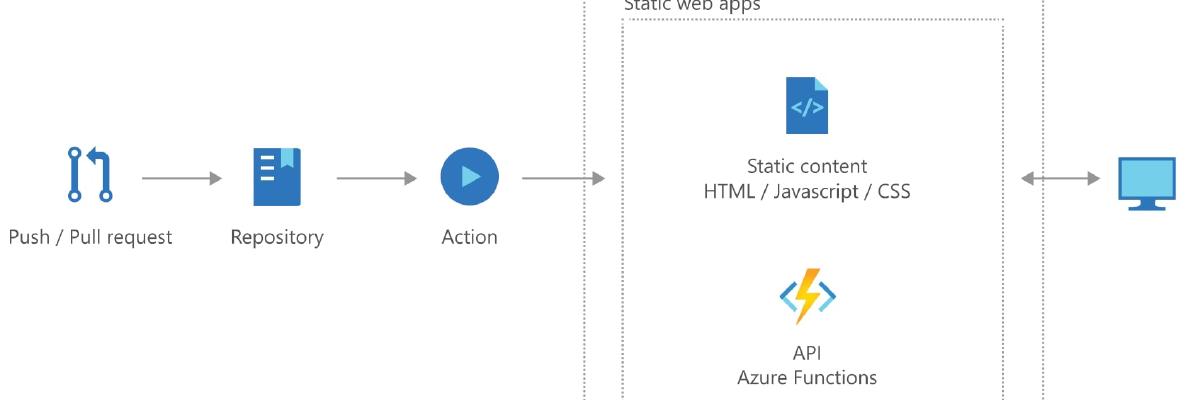
In this post I will talk about Azure Static Web Apps, this is a service to host your static (and lambda functions)
At the moment of writing this post, it’s in a preview, and it’s free.
How to deploy your app, for example, a Vue app.
Go to https://portal.azure.com/ and create a new account if you haven’t one yet.
Into the resource group click in + Create resource
Choose Static Web App (preview)
You must select the subscription, the Resource group to assign this resource, the name of your app (to find it later in the Azure panel), the region where you want to serve the static files (choose one near your clients or users)
You need to link with your Github account and choose the repo (and the branch) to deploy.
Azure will create behalf you a Github Action to build your website and deploy it to SWA.
Something like this
name: Azure Static Web Apps CI/CD
on:
push:
branches:
- main # This action will run on push to main
jobs:
build_and_deploy_job:
if: github.event_name == 'push'
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
name: Build and Deploy Job
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v2
with:
submodules: true
- name: Build And Deploy
id: builddeploy
uses: Azure/static-web-apps-deploy@v0.0.1-preview
with:
azure_static_web_apps_api_token: ${{ secrets.AZURE_STATIC_WEB_APPS_API_TOKEN }}
repo_token: ${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }} # Used for Github integrations (i.e. PR comments)
action: "upload"
app_location: "/" # Path to your app in the web server
api_location: "api" # Api source code path - optional
output_location: "dist"
env:
VUE_APP_MY_VARIABLE: value
# Environment variables needed to build your app
For more information about the actions you can read the official documentation: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/static-web-apps/github-actions-workflow
After doing this the Github action will run after every push to master, build the app, and deploy to azure.
Azure provides you an url to access your website, like *.azurewebsites.net, you can also add your custom domain.
Configuring routes
If you need to configure the routes, for example securing a route to allow only access to your company users, add a fallback route, or create a redirect you need to create a file named routes.json which is in the root directory after the build, in Vue you must store this in the static folder.
For example, this file forces users to must authenticated to access to any route and if the page requested is not found redirects to 200.html
{
"routes": [
{
"route": "/*",
"allowedRoles": ["authenticated"]
}
],
"platformErrorOverrides": [
{
"errorType": "NotFound",
"serve": "/200.html",
"statusCode": 200
}
]
}
Mor info about routes.json https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/static-web-apps/routes
I didn’t mention you can use lambdas to run server-side code (it is not free), but maybe I will write more about that in the future.
To summarizing, Azure Static Web Apps is another option to deploy static web apps, if you are using Azure in your company can be a good option to keep all the infrastructure services on the same platform, and it’s a simple alternative to deploy an App Service
